To obtain an Oriented Bounding Box (OBB) for an object, we first need to retrieve the local Axis Aligned Bounding Box (AABB) and then construct our OBB using a center and an extent vector transformed with the Actor’s world Transform. While the AABB consists of a single Extent vector representing the magnitude on each axis (X, Y, Z), our OBB requires an extent vector per axis.
In the image below, we can visualize:
- In red: the Local space AABB (with the original object inside).
- In blue: the AABB of the object.
- In yellow: our calculated OBB (of our scaled, rotated and translated Actor).
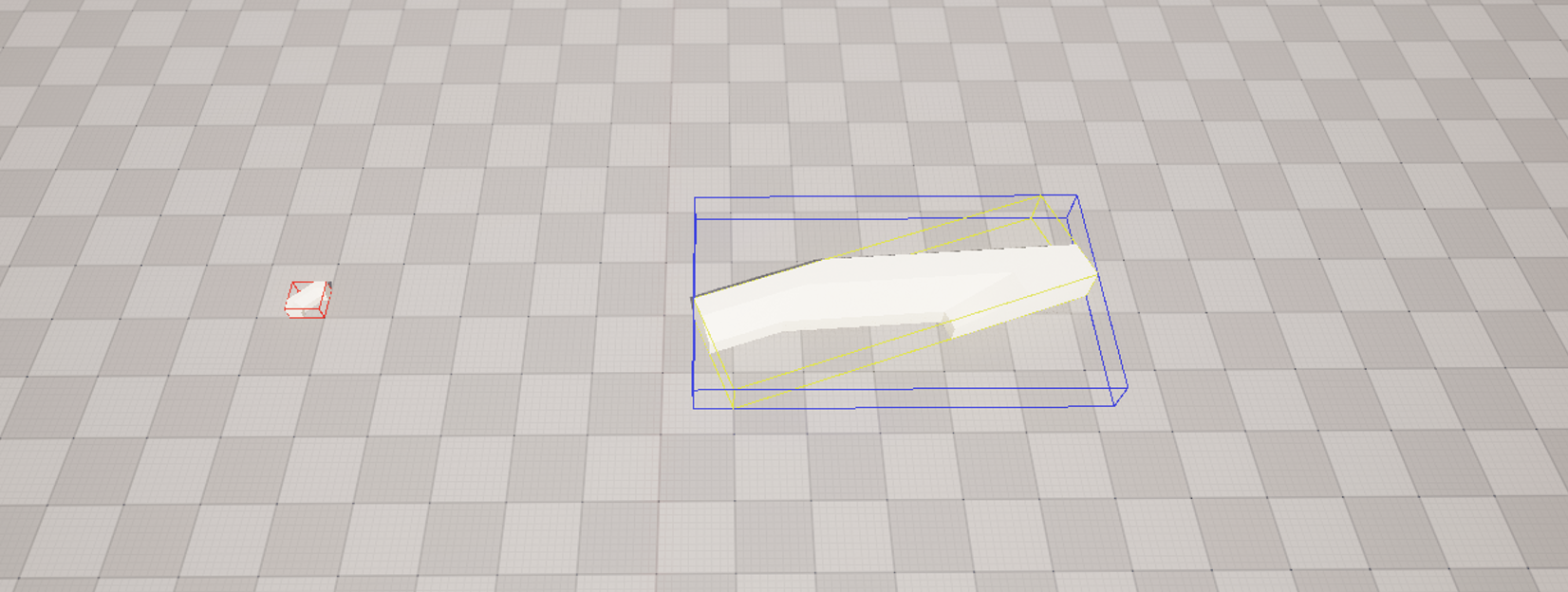
Let’s start by defining the OBB structure:
/**
* @brief Represents an oriented bounding box.
* The extents are measured from the center to the maximum point along each axis.
*/
struct FL0OrientedBox
{
FVector Center;
FVector Forward;
FVector Right;
FVector Up;
FL0OrientedBox()
: Center(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f),
Forward(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f),
Right(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f),
Up(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f)
{
}
};
Now, let’s compute our OBB from an actor:
FL0OrientedBox UL0GameplayLibrary::CalculateActorOrientedBoundingBox(AActor* Actor)
{
if (ensure(Actor) == false)
{
return FL0OrientedBox();
}
// Get the AABB in Local space (aka Object space: such as in the Blueprint viewer). You might want to cache this result as this may be costly.
const FBox Box = Actor->CalculateComponentsBoundingBoxInLocalSpace();
const auto Transform = Actor->GetTransform();
// Get World space Location.
const FVector Center = Transform.TransformPosition(Box.GetCenter());
// And World space extent
const FVector Extent = Box.GetExtent();
const FVector Forward = Transform.TransformVector(FVector::ForwardVector * Extent.X);
const FVector Right = Transform.TransformVector(FVector::RightVector * Extent.Y);
const FVector Up = Transform.TransformVector(FVector::UpVector * Extent.Z);
// Now you have an oriented bounding box represented by a `Center` and three extent vectors.
FL0OrientedBox OrientedBox;
OrientedBox.Center = Center;
OrientedBox.Forward = Forward;
OrientedBox.Right = Right;
OrientedBox.Up = Up;
return OrientedBox;
}
Note that the DrawDebugBox function cannot be used directly because it expects an AABB. However, here’s a custom function that draws an OBB:
void UL0GameplayLibrary::DrawDebugOrientedBox(UWorld* World, const FL0OrientedBox& Box, const FColor& Color,
float LifeTime)
{
const FVector Center = Box.Center;
const FVector Forward = Box.Forward;
const FVector Right = Box.Right;
const FVector Up = Box.Up;
const FVector ExtentsX = Right;
const FVector ExtentsY = Up;
const FVector ExtentsZ = Forward;
const FVector Corner1 = Center + ExtentsX + ExtentsY + ExtentsZ;
const FVector Corner2 = Center + ExtentsX - ExtentsY + ExtentsZ;
const FVector Corner3 = Center - ExtentsX - ExtentsY + ExtentsZ;
const FVector Corner4 = Center - ExtentsX + ExtentsY + ExtentsZ;
const FVector Corner5 = Center + ExtentsX + ExtentsY - ExtentsZ;
const FVector Corner6 = Center + ExtentsX - ExtentsY - ExtentsZ;
const FVector Corner7 = Center - ExtentsX - ExtentsY - ExtentsZ;
const FVector Corner8 = Center - ExtentsX + ExtentsY - ExtentsZ;
DrawDebugLine(World, Corner1, Corner2, Color, false, LifeTime);
DrawDebugLine(World, Corner2, Corner3, Color, false, LifeTime);
DrawDebugLine(World, Corner3, Corner4, Color, false, LifeTime);
DrawDebugLine(World, Corner4, Corner1, Color, false, LifeTime);
DrawDebugLine(World, Corner5, Corner6, Color, false, LifeTime);
DrawDebugLine(World, Corner6, Corner7, Color, false, LifeTime);
DrawDebugLine(World, Corner7, Corner8, Color, false, LifeTime);
DrawDebugLine(World, Corner8, Corner5, Color, false, LifeTime);
DrawDebugLine(World, Corner1, Corner5, Color, false, LifeTime);
DrawDebugLine(World, Corner2, Corner6, Color, false, LifeTime);
DrawDebugLine(World, Corner3, Corner7, Color, false, LifeTime);
DrawDebugLine(World, Corner4, Corner8, Color, false, LifeTime);
}


Leave a Reply